You might have heard about the Climate Commission’s draft plan for New Zealand’s climate action over the next 15 years. This is a crucial opportunity to put a roadmap in place that will allow Aotearoa to play our part in overcoming the climate challenge and ensuring our action will stand with those facing the impacts of climate breakdown right now. It covers a lot, so here we highlight four good things, and five areas for improvement. You can have your say too. The Climate Commission is seeking submissions up until March 28th.
This is a 5–minute read about key areas relevant to Oxfam’s work on global equity and climate justice. To make a submission that covers more areas of what the Climate Commission is asking for feedback on, use the submission guide we prepared with a bunch of other organisations.
4 great things about the Commission’s plan.
1. It confirms New Zealand’s international climate target needs to be boosted.
Something that we’ve long been talking about is that New Zealand’s 2030 target for reducing pollution under the Paris Agreement is inconsistent with limiting warming to 1.5 degrees. The Commission agrees, and recommended that New Zealand ought to do more than the average to reflect our outsized carbon footprint and past contribution to causing climate change. As a developed, relatively wealthy nation, our international target should reflect our fair share of emissions cuts. Last year, we released a report outlining what New Zealand’s fair share would be: at least 99% reductions below 1990 levels by 2030.
2. Permanent native forests are part of the solution.
A key aspect to the Commission’s plans is that relying solely on large pine forests to offset our emissions isn’t desirable or sustainable. As a country we need to cut our pollution at the source. There will still be a big role for forestry to meet our targets, but the Commission envisages much more of forestry’s role in absorbing carbon to be done through permanent native forests, which is great news for our biodiversity.
3. The Commission’s plan confirmed that fossil gas is not a bridge fuel.
Vested interests in the fossil fuel industry have tried to advocate for fossil gas as a ‘bridge’ or ‘transition’ fuel while we decarbonise away from coal. However, the Commission’s analysis shows that it is necessary and possible to cut our pollution from all fossil fuels – coal, oil and gas – in order to meet our targets. We think that shifting from all fossil fuels needs to be faster than the Commission plans for, but overall the Commission’s plan helps confirm that fossil fuels are history and we need to embrace the clean, renewable future once and for all.
4. It highlights climate finance to communities on the frontlines is a necessary part of our international action.
New Zealand’s responsibilities for acting on climate change are not just for cutting our pollution at home, but also supporting communities in the Pacific and beyond that are on the frontlines of climate change to adapt to the impacts they are facing. Currently New Zealand has woefully low levels of climate finance compared to others. The Commission states that climate finance to developing countries can be part of New Zealand contributing to global climate action. This is great, and can potentially supplement our international target, however the focus of this finance should be on adaptation and mitigation, not solely mitigation.
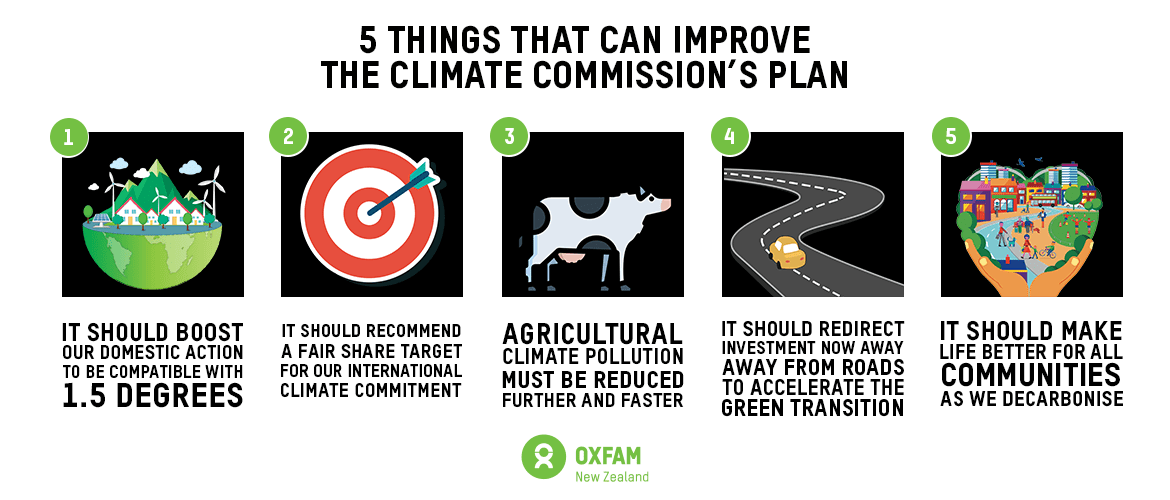
5 things that can improve the Commission’s plan
1. It should boost our domestic action to be compatible with 1.5 degrees (a safe climate future)
We know that the best chance of keeping global heating to 1.5 degrees is by cutting pollution fast in the next 10 years. The most disappointing part of the Commission’s plan is that it is not enough to meet our current Paris Agreement target for 2030. This is the same target the Commission has found to be inconsistent with limiting global heating to 1.5 degrees. We need to increase the pollution cuts in the first two ‘emissions budgets’ drafted by the Commission to set us up for a 2030 pathway consistent with 1.5 degrees. This can be done through making polluters pay for their pollution faster than planned, bringing forward end dates for fossil fuel use, and increasing direct government investment in our decarbonisation rather than relying on incentives.
2. It should recommend a fair share target for our international climate commitment.
It’s great that the Commission found New Zealand’s current international target under the Paris Agreement needs to be boosted. What’s needed now is to increase it in line with our fair share of pollution reductions, so that we don’t hand an unfair burden to developing nations to do our work for us and deal with the impacts. At the moment, the Commission doesn’t recommend what our fair share would be. We need them to recommend a target (or a target range) that would reflect our outsized carbon footprint and historical responsibility for causing climate change so that the government can’t get away with ignoring this advice or fudging the numbers.
3. Agricultural climate pollution must be reduced further and faster.
Farming is New Zealand’s largest polluting industry, contributing to around half of our country’s emissions. In its current form, the Commission’s plan largely lets agricultural emissions off the hook – it’s the area where planned reductions are most clearly not aligned with 1.5 degree pathways and the plan doesn’t anticipate any reductions in production volumes. What we need to do is make our most polluting industries pay for the damage they are causing, and reinvest that revenue in supporting farmers to diversify land uses. Cutting climate pollution from agriculture should include specific and direct regulations (such as bans and caps) on the sources of pollution, including a sinking cap on cow numbers, synthetic fertiliser and imported feed.
4. It should redirect investment now away from roads to accelerate the green transition
We can put much larger direct investment into accelerating the transition in transport and infrastructure. At the moment, the government has spent more on roads and other carbon intensive infrastructure in its Covid recovery spending than on climate friendly initiatives, and Auckland’s 10 year budget for transport being decided on right now is looking like it could do the same. The Commission’s plan only forecasts $190 million per year to be spent on decarbonisation between now and 2025. There are billions of dollars in planned road and urban sprawl spending that could be redirected right now into building public and active transport, reallocating street space, and retrofitting and building energy efficient and accessible housing. There needs to be clear recommendations so the government can change track before polluting investments are locked in.
5. It should make life better for all communities as we decarbonise
It’s critical that taking action to cut our pollution leaves no one behind and takes us closer to a fairer, more equal and just society. The Commission’s report notes lots of ways to mitigate the impact on communities in vulnerable situations, but this needs further work to highlight the opportunities and co-benefits of doing so. One example is the opportunities to build and retrofit housing stock that will address the unacceptable shortage of accessible housing for disabled people; Another is the opportunity for native forests management and planting to move beyond consultation approaches and give management of land back to Maori to uphold Article Two of Te Tiriti or Waitangi. There is no consideration in the report of the adverse impacts of climate change on women and other genders, and the need for gender-responsive climate action. This needs to change.
Hope that’s been useful! Want to learn more? Read the in-depth submission guide prepared by Oxfam and 10 other organisations here: bit.ly/CCCsubmissionguide












